|
Location | Climate
| Geography | Flora and fauna
| Humans
Location
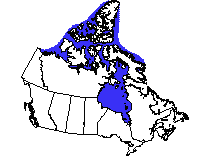
The waters of this marine ecozone nclude Hudson Bay and encompass most
of the water surrounding the islands of Nunavut and Northwest Territories.
Climate
This is the ecozone that saw so many attempts to find the Northwest
Passage to the Pacific Ocean. Long cold winters and short cool summers
make this a cold ecozone; winter temperatures on the surface average
-30ºC, and July only sees an average temperature of 10ºC. Shores are
often scoured by the packs of ice that drift in the brief summer.
Geography
Given their northern location, it is not surprising that the waters
of this ecozone are often covered in ice. During winter, the ice forms
a solid sheet and one can freely walk from island to island. The brief
summer allows the ice to melt and break up, although it still exists
in floating sheets. Average water depths range from 150 to 500 metres.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Only tiny phytoplankton are found throughout the area, although intertidal
zones in the south contain kelp beds.
Animals
Mammals
Only some of the mammals here spend much time out of the water,
such as the polar
bear, walrus,
ringed seal,
bearded seal,
and harp
seal. Beluga,
narwhal,
orca, and bowhead
whale are present in the water.
Birds
Birds in the area
can only take advantage of area of open water during the brief summer.
They include tundra
swans, arctic
terns, northern
fulmars, black
guillemot, and various loons, ducks, geese, gulls, jaegers, and
alcids.
Fish
Arctic cod, arctic char, arctic
cisco, arctic lamprey, pink salmon, and chum salmon are some common
species of fish found in the ecozone.
Molluscs
Four molluscs that are found here are Lacuna
glacialis, Cingula
castanea, Trichotropis
borealis, and Velutina
undata.
Crustaceans
Many crustaceans are found here, including stone
crab, Sclerocrangon
boreas, striped
pink shrimp, and Lebbeus
groenlandicus.
Humans
The mostly Inuit population has a largely subsistence lifestyle, although
mineral and fossil fuel exploration may have large effects in the future.
Waters in James Bay are affected by hydroelectric projects and will
be more affected by population growth in the lands around the southern
part of this ecozone.

|