|
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans | Images
Location
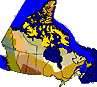
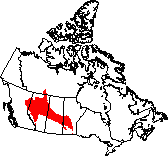
The Boreal Plains are found in the centre of Alberta, extending east
through the centre of Saskatchewan and slightly south of centre Manitoba.
Climate
A more northerly extension of the Prairie ecozone to its south, the
Boreal Plains ecozone endures mean annual temperatures of around freezing.
Summers are short and warm, winters cold. The Rocky Mountains block
much of the moisture, resulting in precipitation of 300mm in the west
to 625mm in the east.
Glaciers from many ice ages
have flattened the landscape, and the large ancient lakes that resulted
from their meltwater have left many dunes and are still present in many
cases as smaller lakes.
Geology
and Geography
 Flat
or slightly rolling terrain is the rule here, and thick soil deposits
overlay Cretaceous shale bedrock. Flat
or slightly rolling terrain is the rule here, and thick soil deposits
overlay Cretaceous shale bedrock.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Much of the Boreal
Plains are covered with forests despite heavy logging. Fires are common,
and many species are very well adapted to them. Dominant tree species
include white
spruce, black
spruce, balsam
fir, jack
pine, tamarack,
white birch,
water birch,
Alaska paper
birch, mountain
alder, trembling
aspen, Pacific willow, Bebb willow, pussy willow, Manitoba maple,
and balsam poplar.
The deciduous species are most commonly found in the south, the coniferous
species to the north. The Saskatoon berry bush is one of the other plant
species found here.
Animals
Extensive
logging has reduced the population and ranges of many species. Wetlands
and rivers have also suffered from pollution, increased water use and
other human activities.
Mammals
Large carnivores in the ecozone include the black
bear, wolf,
and lynx.
The most common large herbivores are elk,
mule deer,
white-tailed
deer, moose,
caribou,
and bison.
Smaller carnivores include the coyote,
least weasel,
river otter,
badger,
striped skunk,
muskrat,
marten,
and fisher.
There are many rodents, such as the northern
pocket gopher, beaver,
woodchuck,
Richardson's
ground squirrel, thirteen-lined
ground squirrel, Franklin's
ground squirrel, least
chipmunk, porcupine,
eastern cottontail,
and snowshoe
hare.
Birds
Characteristic birds of prey include the great
horned owl, boreal
owl, northern
saw-whet owl, short-eared
owl, Cooper's
hawk, red-tailed
hawk, broad-winged
hawk, and turkey
vulture. Some of the songbirds found here are the blue
jay, evening
grosbeak, rose-breasted
grosbeak, ruby-throated
hummingbird, cedar
waxwing, whip-poor-will,
purple finch,
brown creeper,
sedge wren,
and the common crow.
Some other birds of the forest are ruffed
grouse, spruce
grouse, northern
flicker, downy
woodpecker, and pileated
woodpecker. Waterfowl include Franklinís
gull, American
white pelican, common
loon, sandhill crane, western
grebe, wood
duck, ring-necked
duck, northern
pintail, blue-winged
teal, mallard,
gadwall, redhead,
canvasback,
Canada goose,
and whooping cranes, which nest in wetlands in the extreme north of
the ecozone.
Amphibians and reptiles
Two of the amphibian species here are the wood
frog and american
toad. The common
garter snake can also be found.
Fish
Predatory fish here include lake sturgeon, brown
trout, lake trout,
northern pike,
and walleye.
They prey on such species as cisco
(lake herring), lake
whitefish, goldeye, lake chub, emerald shiner, and yellow
perch.
Insects
A few of the insect species found here are the boreal
spittlebug, spring azure, American
copper, monarch butterfly, mourning
cloak, and American
cockroach.
Molluscs
Two species of
molluscs found in the Boreal Plains are the arctic-alpine
fingernail clam and the globular
pea clam.
Humans
When first settled, the Boreal Plains were important for trading companies
and the fur trade. For the past fifty years oil and gas has been the
major economic focus in Alberta. Other natural resources have been important
as well, especially forestry. The three-quarters of a million people
who live in this ecozone are scattered in small communities rather than
the larger urban concentrations found in most southern ecozones.
Images
Dry
Island Buffalo Jump Provincial Park, Alberta
Elk
Island National Park
North
of Valleyview, Alberta
Wood
Buffalo National Park
 
|
|



 Flat
or slightly rolling terrain is the rule here, and thick soil deposits
overlay Cretaceous shale bedrock.
Flat
or slightly rolling terrain is the rule here, and thick soil deposits
overlay Cretaceous shale bedrock.