|
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans | Images
Location
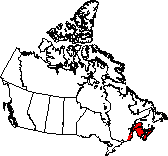
Nova Scotia, New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island are completely within
the Atlantic Maritime ecozone, along with the Gaspe peninsula.
Climate
Covering Quebec's Gaspé peninsula and the entirety of Prince Edward
Island, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, this ecozone's climate is strongly
influence by the Atlantic Ocean, which produces cooler summers and warmer
winters. Winter temperatures average -5ºC and summers average 14ºC,
with coastal areas having slightly warmer winters and cooler summers
than inland. The Atlantic also provides moisture to the region, producing
mean precipitation of 900mm a year inland and over 1500mm a year on
the coast; this high precipitation also means that the region has more
storms than anywhere else in the country.
Geology
and Geography
 Geologically,
this region is a mix of sedimentary and igneous bedrock. Inhospitable
igneous highlands form much of the interior of the many peninsulas that
form this ecozone. Acid soils found here support vast forests, but are
poor for agriculture, and the cold wet climate prevents many people
from living in this part of the ecozone. The coastal lowlands, overlying
sedimentary bedrock, are far more accessible, have better soils for
agriculture, and a milder climate. Not surprisingly, the lowlands are
where most of the ecozone's human population lives. Geologically,
this region is a mix of sedimentary and igneous bedrock. Inhospitable
igneous highlands form much of the interior of the many peninsulas that
form this ecozone. Acid soils found here support vast forests, but are
poor for agriculture, and the cold wet climate prevents many people
from living in this part of the ecozone. The coastal lowlands, overlying
sedimentary bedrock, are far more accessible, have better soils for
agriculture, and a milder climate. Not surprisingly, the lowlands are
where most of the ecozone's human population lives.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Little old growth forest remains in this ecozone after centuries of
farming and agriculture. Nevertheless, it is very densely forested with
second- and third-growth forests. The forests include such conifers
as red spruce,
black spruce,
white spruce,
balsam fir, red
pine, jack pine,
eastern white pine,
tamarack, eastern
white cedar, and
eastern hemlock.
The deciduous trees here include yellow
birch, white
birch, paper
birch, sugar
maple, red maple,
striped
maple, balsam poplar, pin
cherry, speckled
alder, beech, black
ash, white ash,
butternut, ironwood,
basswood, white
elm, and red
oak. Just a few of the other plants in the Atlantic Maritime are
the steeplebush, blueberry, sphagnum moss, kalmia heath, smooth
serviceberry (smooth juneberry), violets, wild lupins, starflower,
trailing arbutus, lady slipper, pitcher plant, ostrich
fern, and purple
loosestrife, which was introduced and has become quite a problem
in the area's waterways.
Animals
Mammals
The only large carnivores
found here are the black
bear, lynx,
and bobcat.
The most common large herbivores are the whitetail
deer and moose.
Small carnivores in the area include red
fox, muskrat,
raccoon,
striped skunk,
marten,
fisher,
coyote,
mink and river
otter. Many small herbivores, including the eastern
chipmunk, beaver,
porcupine,
snowshoe
hare, northern
flying squirrel, woodchuck,
and southern bog
lemming. The numerous species of aquatic mammals found in the waters
off the coast are extremely popular among tourists, and include harbour
seal, gray
seal, hooded
seal, harp
seal, orca,
northern
bottlenosed whale, and blue
whale.
Birds
Characteristic birds of prey include osprey,
Cooper's hawk,
broad-winged hawk,
common nighthawk,
northern goshawk,
northern saw-whet owl,
short-eared owl,
and long-eared owl.
A few of the many songbirds are the red-winged
blackbird, ruby-throated
hummingbird, cedar
waxwing, whip-poor-will,
purple finch, brown
creeper, black-billed
cuckoo, whip-poor-will,
blue jay,
eastern bluebird,
rose-crested
grosbeak, and cardinal.
Other birds of the forest include the ruffed
grouse, spruce
grouse, northern
flicker, downy
woodpecker, and pileated
woodpecker. Waterfowl include the great
blue heron, Canada
goose, American
bittern, common
snipe, ring-necked
duck, wood duck,
American black duck,
northern pintail,
and blue-winged teal.
Seabirds and shorebirds of the Atlantic Maritime ecozone include the
great cormorant,
double-crested
cormorant, Atlantic
puffin, common
murre, thick-billed
murre, black
guillemot, razorbill,
herring gull,
spotted sandpiper, common
snipe, and killdeer.
Reptiles and Amphibians
Frogs and toads of the region are the American
toad, northern
leopard frog, mink
frog, green frog,
pickerel frog,
wood frog, and
the tiny but extremely vocal spring
peeper. Five species of salamanders and newt are found here: yellow-spotted
salamander, blue-spotted
salamander, dusky
salamander, eastern
redback salamander, and eastern
newt. There are more species of marine turtles (loggerhead
turtle, leatherback
turtle, and Atlantic
ridley) than freshwater turtles (common
snapping turtle and wood
turtle) here. All four species of snakes are harmless to humans.
They include the maritime
garter snake, smooth
green snake, redbelly
snake, and ringneck
snake.
Fish
Some of the predatory fish of the ecozone are brook trout and Atlantic
tomcod. They prey upon the rainbow smelt, golden shiner, common shiner,
creek chub, and mummichog, among others. A few of the marine species
that return to freshwater to spawn include sea lamprey, Atlantic sturgeon,
alewife, Atlantic salmon, and American eel. Species that are found in
the marine waters off the coast are covered in the Atlantic
Marine and Northwest
Atlantic Marine ecozones.
Crustaceans
The waters of the region are well known for their many lobster, crab
and shrimp fisheries.
Molluscs
A few of the species found here are the brown
mystery snail, valve
snail, ordinary
spire snail, eastern
physa, and eastern
elliptio. In addition, the waters off the coast are known for their
clams and scallops.
Insects
Some of the insects in the Atlantic Maritime, both famous and obscure,
are the German
cockroach, American
cockroach, eastern
metallic green wood borer, European
earwig, boreal
spittlebug, spring
azure, American
copper, monarch
butterfly, mourning
cloak, eastern
black swallowtail, and migratory
grasshopper.
Humans
Fishing was the base of the economy in this ecozone for centuries, until
overfishing caused the crash of several major fish stocks. Agriculture
is only possible where good soil is available (potato farms on PEI are
the most famous), but is still an important part of the economy. Forestry
has also been important economically, and most of the forests here have
been logged at least once. Half of the 2.5 million people who live here
live in rural areas, far above the national average.
Images
Blacks
Harbour, Nova Scotia
Cape
Breton Island, Nova Scotia
Cape
Breton, Nova Scotia
From
Louisbourg Lighthouse, Nova Scotia
Gooseberry
Bay, Nova Scotia
Gooseberry
Bay, Nova Scotia
Gooseberry
Bay, Nova Scotia
Gooseberry
Bay, Nova Scotia
Gooseberry
Bay, Nova Scotia
Near
Louisbourg Lighthouse, Nova Scotia
Island
Near Louisbourg, Nova Scotia
Near
Louisbourg, Nova Scotia
Near
Louisbourg, Nova Scotia
Nova
Scotia
Nova
Scotia Lakes
Near
Louisbourg Lighthouse, Nova Scotia
 
|
|