|
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans | Images
Location
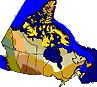
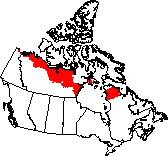
The Southern Arctic extends across the northern edge of much of the
continental Northwest Territories and Quebec, bordered by the tree line
to the south and the Northern Arctic ecosystem to the north.
Climate
This far north, the summers are short and cool, while winters are long,
cold, and dark. Summers average 5șC, while winters vary between an average
of -28șC near the Mackenzie Delta to -18șC in northern Quebec.
Precipitation in the west
is low, approximately 250mm per year, and only rises to 500mm at the
eastern end of the ecozone. Permafrost is found throughout the region,
sometimes only a few centimetres below the surface.
Geology
and Geography
 The
look of the Southern Arctic is largely the result of glaciers. As the
glaciers expanded and moved south, they carried rocks and earth with
them. Exposed bedrock, which may have been exposed by the scraping of
the glaciers, still bears scratch marks from rocks dragged across them
by the glaciers' advance. Rocks up to the size of houses were torn from
the bedrock and carried by the glaciers, sometimes a few metres and
sometimes a few thousand kilometres. When they ended up far from home,
these rocks are appropriately known as "glacial erratics". The
look of the Southern Arctic is largely the result of glaciers. As the
glaciers expanded and moved south, they carried rocks and earth with
them. Exposed bedrock, which may have been exposed by the scraping of
the glaciers, still bears scratch marks from rocks dragged across them
by the glaciers' advance. Rocks up to the size of houses were torn from
the bedrock and carried by the glaciers, sometimes a few metres and
sometimes a few thousand kilometres. When they ended up far from home,
these rocks are appropriately known as "glacial erratics".
When the glaciers retreated
from this area about 8 500 years ago, soil and rocks were deposited
in huge amounts, resulting in all types of characteristic landscape
features. The bedrock here is mostly Precambrian granite, which is exposed
throughout the area.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
The southern edge of the Southern Arctic is the tree line, a transition
zone north of which no full-sized trees are found. Anything north of
the tree line is defined as the arctic. The low temperatures, low precipitation,
and high winds in most of the ecozone encourages low plants. Stunted
forms of tree species such as dwarf
birch, alder, arctic willow, white
spruce, black
spruce, tamarack,
least willow, net-veined willow and blue-green willow grow here.
Other plant species that
grow in the Southern Arctic include the heath, lichen, northern Labrador
tea, Dryas, sedge species, sphagnum moss, cottongrass, ericaceous
shrubs, Vaccinium, fragrant shield fern, shrub birch, crowberry,
bearberry, moss campion, blueberry, mountain cranberry, cloudberry,
and alpine club moss.
Animals
North of the tree line, life becomes difficult for animals as well as
plants. Most impressive of the animals here is the caribou and their
massive migrations. Many birds also migrate, though they fly over the
ecozone as much as land in it.
Mammals
Larger carnivores in the Southern Arctic include the grizzly
bear, black
bear and polar
bear as well as wolves.
The most common large herbivores are barren-ground
caribou, woodland
caribou, moose,
and muskox.
Smaller carnivores, such as the red
fox, arctic
fox, lynx,
coyote,
weasels, wolverine
and ermine
prey on smaller herbivores, which include the arctic
ground squirrel, brown
lemming, showshoe
hare, arctic
hare masked
shrew,
tundra redbacked
vole , and beaver.
Aquatic mammals include walruses,
various seals, belugas,
narwhals,
and white
whales.
Birds
Many birds migrate here in the spring to breed, but spend the long cold
winters further south. Many others pass over the Southern Arctic during
their migrations to breed still further north. Four characteristic birds
of prey include the snowy
owl, gyrfalcon,
osprey, and
rough-legged
hawk. Waterfowl that can be found here include Canada
goose, yellow-billed
loon, arctic
loon, red-throated
loon, tundra
swan, whistling swan, snow goose, oldsquaw
duck and sea ducks. Some common shorebirds and seabirds in the Southern
Arctic are the semi-palmated
plover, northern
phalarope, lapland
longspur, parasitic
jaeger, and semi-palmated plover. Songbirds also live here, including
the snow bunting,
raven, American
tree sparrow, and hoary
redpoll. Willow
ptarmigan, rock
ptarmigan and spruce
grouse are a few of the ground-dwelling birds.
Reptiles and Amphibians
This ecozone is too harsh for either reptiles or amphibians to live
in.
Molluscs
Three species of molluscs that live in the Southern Arctic are the muskeg
stagnicola, arctic-alpine
fingernail clam, and globular
pea clam.
Humans
Extremely few people (only about 10 000) live here, and the majority
of the population is Inuit. Most people live through subsistence activities,
such as hunting, trapping and fishing, though gas and oil exploration
also provide a living for some, as does tourism.
Images
Wetlands, Tuk, Yukon
 
|
|


 The
look of the Southern Arctic is largely the result of glaciers. As the
glaciers expanded and moved south, they carried rocks and earth with
them. Exposed bedrock, which may have been exposed by the scraping of
the glaciers, still bears scratch marks from rocks dragged across them
by the glaciers' advance. Rocks up to the size of houses were torn from
the bedrock and carried by the glaciers, sometimes a few metres and
sometimes a few thousand kilometres. When they ended up far from home,
these rocks are appropriately known as "glacial erratics".
The
look of the Southern Arctic is largely the result of glaciers. As the
glaciers expanded and moved south, they carried rocks and earth with
them. Exposed bedrock, which may have been exposed by the scraping of
the glaciers, still bears scratch marks from rocks dragged across them
by the glaciers' advance. Rocks up to the size of houses were torn from
the bedrock and carried by the glaciers, sometimes a few metres and
sometimes a few thousand kilometres. When they ended up far from home,
these rocks are appropriately known as "glacial erratics".