|
Location | Climate
| Geology and geography | Flora and
fauna | Humans
Location
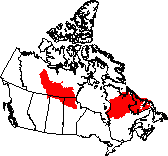
This ecozone stretches eastward from the Taiga Plains, just south of
the Southern Arctic. It is interrupted by Hudson Bay and the Hudson
Plains, but then continues to the Atlantic.
Climate
This ecozone has short summers with long days and cold, long winters
with long nights. Average annual temperatures are just below freezing,
and mean summer temperatures are at most 11ºC. Precipitation ranges
from 200mm a year in the west to 1000mm on the Labrador coast.
Geology
and Geography
As part of the Canadian Shield, the bedrock here is extremely old, and
the region north of Great Slave Lake contains the oldest rock on the
planet, over four billion years old. The terrain here is either flat
or rolling hills. Advancing and retreating glaciers have scraped the
ground bare at several points in the past, and the millions of depressions
that have been left are now lakes. Much of the flat lands are temporarily
or permanently waterlogged.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
A patchwork of wetlands, forests, meadows, and shrublands covers this
area. The northern edge of the ecozone is delineated by the tree line,
and it is north of this that the more typical arctic tundra begins.
Trees in the Taiga Shield
include black spruce,
jack pine, green
alder, paper
birch, willow, tamarack,
white spruce,
balsam fir, trembling
aspen, balsam poplar, white
birch, and dwarf
birch.
Other plants in the area
include ericaceous shrubs, cottongrass, lichen, moss, sedge, sphagnum
moss, Labrador tea, feathermoss, northern Labrador tea, yellow pond
lily, cattail, water parsnip, water smartweed, water horsetail, water
arum, marsh five-finger, ground juniper, kinnikinick, lichens, goldenrod,
grass of Parnassus, shrubby cinqfoil, sweet
gale, northern commandra, wild rose, wood
horsetail, wild chives, twinflower, feathermoss, soapberry, cupidberry,
crowberry, bearberry, high-bush cranberry, fireweed, fire snag, rock
harlequin, fragrant shield fern, creeping juniper, prickly saxifrage,
mountain cranberry, and gooseberry.
Animals
Mammals
About fifty species of mammals are found in the Taiga Shield, including
the large herbivores barren-ground
caribou, woodland
caribou, and moose.
Wolves,
black
and grizzly
bears and the lynx
are the larger predators. Smaller predators include the coyote,
red and
arctic fox,
muskrat,
wolverine,
weasel, mink, marten,
otter, and least
weasel. The smaller herbivores include the snowshoe
hare,
beaver, brown
lemming, red-backed vole,
northern red-backed vole, and red
squirrel.
Birds
Spring migration brings a multitude of bird species through this region,
including various ducks, geese, loons and swans. Some stay, but others
continue north to the arctic to breed. Representative birds of prey
are the osprey
and bald
eagle. Shorebirds
and seabirds found here include northern
phalarope, Bonaparte’s
gull, arctic
tern, greater
scaup, mew gull,
Characteristic waterfowl are the arctic,
pacific, and red-throated
loons, red-breasted
merganser, and the green-winged teal. Forest birds in the ecozone
include northern
shrike, tree
sparrow, gray-cheeked
thrush, raven,
red-breasted merganser, red-winged
blackbird, yellow
warbler, common
redpoll, white-crowned
sparrow, flicker,
and yellow-rumped
warbler. Two representative ground-dwelling birds are the spruce
grouse and willow
ptarmigan.
Reptiles and Amphibians
Three species of amphibians, the mink
frog, wood frog,
and blue-spotted
salamander live here, but there are no reptiles.
Invertebrates
The American
copper butterfly is found here, as are the molluscs muskeg
stagnicola, arctic-alpine
fingernail clam, and globular
pea clam.
Humans
This ecozone is more developed than others to the north of it, thanks
to hydroelectric development and mining. It is also more densely populated,
with 340 000 people, 60% of whom are First Nations. Settlements along
the coast arose during the time of the fur trade, but later settlement
has been largely dictated by mining. Most of the urban areas still have
untouched land nearby, and subsistence activities such as hunting, trapping
and fishing are still common.
 
|
|