|
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans | Images
Location
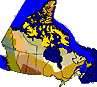
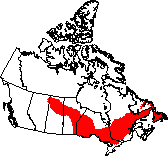
The Boreal Shield covers a wide swath from Alberta to Newfoundland,
south of the Taiga Shield and Hudson Plains and north of various ecozones,
including the Boreal Plains, Mixedwood Plains, and Atlantic Maritime.
Climate
Largest of Canada's ecozones, the Boreal Shield provides the images
of exposed bedrock, endless forests, and rushing rivers that characterize
the image that much of the world (as well as many Canadians) has of
Canada. Summers have roughly the same average temperature throughout
the area, about 13ºC. The maritime influence in the east gives it a
milder winter, with a mean temperature of about -1ºC, while the western
edge suffers through average winter temperatures of -20ºC. Precipitation
in the west is low, about 400mm a year, but it can be a high as 1600mm
a year in some areas of Newfoundland, largely due to its position in
the Atlantic.
Geology
and Geography
 This
ecozone is named after the intersection of the boreal forest and the
Canadian Shield, and the Precambrian granite bedrock of the latter is
commonly exposed here. This may have once been a soaring mountain range,
judging by its tumultuous geological past, but that was a billion years
ago, and all that is left now is rolling hills. Glaciers swept over
this area many times, and the resulting series of depressions and deposits
have given rise to the millions of lakes and wetlands in the region. This
ecozone is named after the intersection of the boreal forest and the
Canadian Shield, and the Precambrian granite bedrock of the latter is
commonly exposed here. This may have once been a soaring mountain range,
judging by its tumultuous geological past, but that was a billion years
ago, and all that is left now is rolling hills. Glaciers swept over
this area many times, and the resulting series of depressions and deposits
have given rise to the millions of lakes and wetlands in the region.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Forest fires create a patchwork of forest types in different stages
of recovery from the fire. Trees to the north are coniferous, but broadleaf
trees appear further south and trees normally found in much warmer climates,
such as the yellow birch and sugar maple, can be found in the south
of the ecozone. Bogs and other wetlands, some of the most diverse and
productive areas in the Boreal Shield, cover one-fifth of the land.
Tree species that can be found here include the white
spruce, black
spruce, balsam
fir, tamarack,
trembling aspen,
balsam poplar, white pine, red
pine, jack
pine, eastern
white pine, red maple, mountain maple, eastern
red cedar, eastern
hemlock, black
ash, speckled
alder, pin cherry, paper
birch and white
birch. Some of the other plants that grow here are ericaceous shrubs,
sphagnum moss, willow, alder, Labrador tea, blueberry, bog rosemary,
feathermoss, cottongrass, sedges, kalmia heath, high bush cranberry,
baneberry, wild sarsaparilla, bunchberry, shield fern, goldenrod, water
lilies and cattails.
Animals
Mammals
Some of the characteristic
large herbivores of the region include woodland
caribou, barren-ground
caribou, white-tailed
deer, and moose.
The larger carnivores in the Boreal Shield are the black
bear, lynx,
bobcat,
and wolf.
Small herbivores and herbivores include raccoon,
striped skunk,
eastern chipmunk,
beaver,
muskrat,
showshoe hare,
red-backed vole, red
squirrel, least
chipmunk, porcupine,
woodchuck,
southern bog
lemming and arctic
hare. They are in turn preyed upon such smaller carnivores as the
marten,
short-tailed
weasel, fisher,
ermine,
mink, river
otter, coyote,
and red fox.
Aquatic mammals found off
of the eastern coast of the ecozone include grey
seal, harp
seal, hooded
seal, ringed
seal , sperm
whale, orca,
Atlantic
pilot whale, fin
whale, blue
whale, northern
right whale, bowhead
whale,and humpback
whale.
Birds
Birds of prey in this ecozone include the boreal
owl, great horned
owl, hawk owl,
bald eagle,
red-tailed hawk,
turkey vulture,
and broad-winged
hawk. The yellow
rumped warbler, blue
jay, evening
grosbeak, gray
jay, common
nighthawk, raven,
mourning dove,
cardinal, wood
thrush, rock
ptarmigen,
willow ptarmigan
and white-throated
sparrow are just a few of the songbirds found here. The forests
hold such species as spruce
grouse, ruffed
grouse, sharp-tailed
grouse, and the pileated
woodpecker. Spring brings large flocks of waterbirds to nest and
breed in the wetlands or just to feed for the rest of their migration
further north. They include the common
loon, sandhill cranes, hooded
merganser, American
black duck, wood duck, Canada
goose, great
blue heron, ring-necked
duck, and bufflehead.
Shorebirds and seabirds found off the eastern coast include the herring
gull, double-crested
cormorant, and Atlantic
puffin, along with various murre, eider, tern and pelican species.
Reptiles and Amphibians
Many species of reptiles and amphibians live in the Boreal Shield. Some
of the frogs and toads include the spring
peeper, wood
frog, mink frog,
and northern leopard
frog. Yellow-spotted
salamanders,
blue-spotted
salamanders, eastern
redback salamanders, and eastern
newts can be found in moist areas. The common
snapping turtle and painted
turtle are two of the turtle species that live in the ecozone. Two
types of garter snake, the maritime
garter snake and common
gartern snake, as well as the redbelly
snake, make their home here.
Fish
Predatory fish in the ecozone include the lake sturgeon, brook trout,
lake trout, northern pike, muskellunge, largemouth bass, sauger, and
walleye. Some of the fish that they prey upon include cisco, (lake herring),
blackfin cisco, lake whitefish, rainbow smelt, lake chub, golden shiner,
and yellow perch. Anadramous fish, which live in the ocean but enter
freshwater to spawn, include the silver lamprey, northern brook lamprey,
american brook lamprey, sea lamprey, alewife and Atlantic salmon.
Molluscs
The valve snail,
ordinary spire
snail, eastern
elliptio, arctic-alpine
fingernail clam, and globular
pea clam are just a few of the mollusc species in the Boreal Shield.
Insects
Insects are common in the
Boreal Shield; some of the species include the German
cockroach, red
turpentine beetle, boreal
spittlebug, spring azure, American
copper, monarch butterfly, mourning
cloak, and bush
katydid.
Humans
The extensive waterways in the Boreal Shield were the roads of the fur
trade. More recently, some rivers have been altered and degraded by
mining, hydroelectric development, and logging practices, though many
are still relatively unaffected. Insect control, monoculture tree plantings,
control of natural forest fires and acidification of the lakes and soil
all affect the natural system, but in many cases the long-term effects
are unclear. The current population is approximately three million.
Images
Laurentians,
Quebec
Cheemo
Lake, Quebec
Shawbridge
area, Quebec
Saguenay
Fjord, Quebec
Lower
Laurentians, Quebec
Near
Shawbridge, Quebec
Cheemo
Lake, Quebec
Jumeaux,
Quebec
Lower
Laurentians, Quebec
 
|
|



 This
ecozone is named after the intersection of the boreal forest and the
Canadian Shield, and the Precambrian granite bedrock of the latter is
commonly exposed here. This may have once been a soaring mountain range,
judging by its tumultuous geological past, but that was a billion years
ago, and all that is left now is rolling hills. Glaciers swept over
this area many times, and the resulting series of depressions and deposits
have given rise to the millions of lakes and wetlands in the region.
This
ecozone is named after the intersection of the boreal forest and the
Canadian Shield, and the Precambrian granite bedrock of the latter is
commonly exposed here. This may have once been a soaring mountain range,
judging by its tumultuous geological past, but that was a billion years
ago, and all that is left now is rolling hills. Glaciers swept over
this area many times, and the resulting series of depressions and deposits
have given rise to the millions of lakes and wetlands in the region.