|
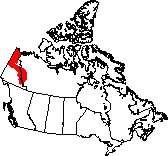
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans
| Images
Location
The Taiga Plains are centered around the Mackenzie River in the western
Northwest Territories, bordered by the mountains to the west, the arctic
to the east, and the boreal forests of the boreal plains to the south.
Climate
Like the Taiga Shield to its east, the Taiga Plains has short, cool
summers and long, cold winters. Mean summer temperatures range from
7ºC in the north to 14ºC in the south. Winter brings averages of -26ºC
in the Mackenzie delta and a relatively mild -15ºC in the portion contained
in Alberta and British Columbia. Snow and freshwater ice lasts for six
to eight months, and permafrost is widespread. There is generally little
rainfall here, only 200-500mm a year.
Geology
and Geography
 Geologically,
this ecozone is primarily horizontally layered sedimentary rock; limestone,
shale, and sandstone. The largest river in the country, the Mackenzie,
flows through this ecozone and dominates its west, while the east is
in turn dominated by the Great Slave and Great Bear lakes. Most of the
terrain is flat or slightly rolling, but where the river or its tributaries
have cut through the ground, canyons hundreds of metres deep can be
found. The permafrost leads to large areas being waterlogged and remnants
of glacier activity make the landscape more varied. Geologically,
this ecozone is primarily horizontally layered sedimentary rock; limestone,
shale, and sandstone. The largest river in the country, the Mackenzie,
flows through this ecozone and dominates its west, while the east is
in turn dominated by the Great Slave and Great Bear lakes. Most of the
terrain is flat or slightly rolling, but where the river or its tributaries
have cut through the ground, canyons hundreds of metres deep can be
found. The permafrost leads to large areas being waterlogged and remnants
of glacier activity make the landscape more varied.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Fires are fairly common, and many species are especially adapted to
it, resulting in a patchwork of forest types where each patch is at
a different stage of recovery from fire. Trees in the Taiga Plains include
paper birch,
willows, trembling
aspen, tamarack,
green alder,
white spruce,
balsam poplar, lodgepole
pine, jack pine,
dwarf birch,
black spruce,
and balsam fir.
Some of the smaller plants that grow here are fire snag, wild rose,
Labrador tea, bearberry, sedges, eriacaceous shrubs, cottongrass, moss,
sphagnum moss, feathermoss, bog cranberry, and blueberry.
Animals
Mammals
The black bear,
lynx,
and wolf
are the only large carnivores to be found here; smaller carnivores include
red fox,
ermine,
and marten.
Large herbivores include woodland
caribou, wood
bison, moose,
and barren-ground
caribou, while snowshow
hare, red
squirrel, arctic
ground squirrel are some of the smaller herbivores.
Birds
Some of the most common birds of prey here, the bald
eagle, peregrine
falcon, and osprey,
are fish-eaters, though the hawk owl is not. Waterfowl, most of whom
migrate to the Taiga Plains in spring and summer, include the red-throated
loon, ring-necked
duck, greater
scaup, canvasback,
and all manner of other ducks, geese and swans. Some ground-dwelling
birds are the sharp-tailed
grouse and willow
ptarmigan, while some common birds of the forest include the raven,
gray
jay, boreal
chickadee, common
raven, and common
redpoll.
Reptiles and Amphibians
This region is too far north for reptiles, but the western
toad, striped
chorus frog, and wood
frog can be found here.
Fish
Fish that can be found in the lakes and rivers of the region include
arctic lamprey, lake trout, lake and mountain whitefish, arctic cisco,
longnose sucker, arctic grayling, dolly varden, burbot, walleye, and
northern pike.
Invertebrates
The large numbers of insects in this ecozone provide food for the insectivorous
birds that come here to feed and breed. Molluscs like the muskeg
stagnicola, arctic-alpine
fingernail clam, and globular
pea clam live in the waters of this ecozone.
Humans
Most settlements in the Taiga Plains are located by rivers, and most
of the landscape has been virtually untouched by human activity. A majority
of the 22 000 people who live here make their living through subsistence
activities, but petroleum exploration, mining, and forestry also take
place.
Images
Beaver
pond, Keg River, Alberta
Beaver
pond and lodge, Keg River, Alberta
 
|
|