|
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans | Images
Location
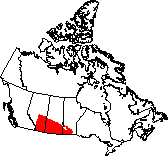
The Prairies cover the south of Alberta, Manitoba and Saskatchewan.
Climate
The Prairies are the northernmost branch of the Great Plains of North
America and the most altered of the ecozones. The mountains to the west
block much of the precipitation that would otherwise fall. That and
the high winds make this ecozone very dry, although precipitation does
generally increase towards the east. Temperatures are extreme due to
the lack of access to the ocean's buffering. Winter temperatures average
-10ºC and summers average 15ºC.
Geology
and Geography
 Glaciation
has left its mark on the Prairies, flattening the landscape and leaving
deposits from inland seas left behind by melting glaciers. These deposits
are now the fertile plains that largely define the Breadbasket of Canada.
Huge numbers of small temporary wetlands form in years with high precipitation.
Gas and oil is plentiful in the region. Glaciation
has left its mark on the Prairies, flattening the landscape and leaving
deposits from inland seas left behind by melting glaciers. These deposits
are now the fertile plains that largely define the Breadbasket of Canada.
Huge numbers of small temporary wetlands form in years with high precipitation.
Gas and oil is plentiful in the region.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Almost 95% of the Prairies have been converted into farmland, with predictable
effects on the original plant populations. Trees and shrubs are most
commonly found in the eastern region.
Trees found in the Prairies include white spruce, black spruce, balsam
fir, tamarack, water
birch, bebb
willow, peachleaf
willow, bebb
willow, peachleaf
willow, wolf willow, lodgepole pine, box elder, choke cherry, black
cottonwood, eastern
cottonwood, bur oak, trembling aspen, and balsam poplar. Just a
few of the other plants that grow here are spear grass, wheat, blue
grama grass, sagebrush, yellow cactus, prickly pear, buckbrush, chokecherry,
Saskatoon berry
bush, alkali grass, wild barley, red sampire, sea blite, Parry oat
grass, June grass, yellow bean, sticky geranium, bedstraw, chickweed,
needle grass, thread grass, snowberry, American
silverberry, rose, silverberry, dryland sedge, black hawthorn, greasewood,
plains larkspur
, death camas, wild lupine, smooth aster, prairie sedge, and cattail
.
Animals
The widespread alteration of the natural habitat has resulted in diminished
populations and ranges of many animals, and the Prairies contain a disproportionate
number of threatened and endangered species.
Mammals
The only large carnivore in the Prairies is the black
bear. Large herbivores include whitetail
deer (a recent invader), mule
deer, pronghorn
antelope, elk,
and moose.
Small carnivores include coyote,
badger,
red fox,
longtail weasel,
mink, river
otter, black-footed
ferret, and striped
skunk. Rodents are numerous, such as the black-tailed
prairie dog, white-tailed
jack rabbit, snowshoe
hare, Richardson’s
ground squirrel, Franklin’s
ground squirrel, thirteen-lined
ground squirrel, least
chipmunk, northern
pocket gopher, Wyoming
pocket mouse, ord
kangaroo rat, white-footed
mouse and beaver.
Birds
Some of the birds of prey are the ferruginous
hawk, red-tailed
hawk, Swainson’s
hawk, burrowing
owl, northern saw-whet
owl, short-eared
owl, long-eared
owl, and turkey
vulture. Songbirds include black-billed
magpie, northern
oriole, Audubon’s
warbler, grasshopper
sparrow, lark sparrow,
ruby-throated hummingbird,
cedar waxwing,
lark bunting, chestnut-collared
longspur, and black-billed
cuckoo. Birds of the forest that are found here include ruffed
grouse, sharp-tailed
grouse, sage grouse,
northern flicker,
downy woodpecker,
red-headed woodpecker,
and western meadowlark.
Some of the waterfowl found here are the American
avocet, great
blue heron, snow
goose, Canada
goose, northern
pintail, blue-winged
teal, mallard,
gadwall, redhead,
western grebe,
lesser scaup,
ring-necked duck,
canvasback, Eskimo
curlew, piping
plover, and whooping
crane.
Reptiles
and Amphibians
Among the amphibians that can be found here are the northern
leopard frog, striped
chorus frog, plains
spadefoot, american
toad, great plains
toad, and tiger
salamander. The area has several species of snakes and lizards,
including the plains
garter snake, gopher
snake, western
rattlesnake, western
terrestrial garter snake, short-horned
lizard, and prairie
skink.
Fish
Predatory fish in the Prairie waterways include northern
pike, carp,
sauger, and sauger.
They prey on such fish as the lake
whitefish, goldeye,
lake chub, brassy
minnow, emerald
shiner and yellow
perch.
Insects
Just a few of the insects are the German
cockroach, boreal
spittlebug, silver-spotted
skipper, spring
azure, American
copper, monarch
butterfly, mourning
cloak, eastern
black swallowtail, migratory
grasshopper, and pallid-winged grasshopper.
Molluscs
Three of the mollusc species in the Prairies are the valve
snail, umbilicate
promenetus, and globular
pea clam.
Humans
The Prairies are the most altered of the ecozones. Agriculture covers
almost all of the land, and almost none of the original ecosystems are
left aside from tiny remnants. Despite the huge amounts of land given
over to farming, farmers comprise less than 10% of the four million
people, and 80% of the population lives in urban areas. Mining and services
are the employers of most of the population.
Images
Canola
field
Drumheller badlands
South Saskatchewan river
Old Man river
Near Camrose, Alberta
 
|
|