|
Location
| Climate | Geology and geography
| Flora and fauna | Humans
Location
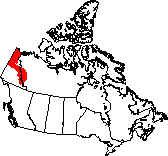
This ecozone extends along most of the border between the Yukon and
Northwest Territories.
Climate
The Taiga Cordillera contains the northernmost of the Rocky mountains
in Canada and also some of its highest waterfalls, deepest canyons and
wildest rivers. Mountains block much of the precipitation, which averages
250 to 300mm per year. Its northerly position gives it cold winters
(-22ºC average temperature) with very short days and short cool summers
(average temperature 8ºC). Snow lasts on the ground for six to eight
months of the year.
Geology
and Geography
Most of the ecozone is covered with steep mountains and narrow valleys,
although the northwest contains wetlands and rolling hills and the north
contains tundra; this tundra is above the treeline, so only smaller
plants are found there.
Flora
and Fauna
Plants
Location on the slopes of the ecozone determines which plants are to
be found. Western-facing slopes recieve more precipitation than those
that face the east, while southern slopes are warmer, brighter and drier
than north-facing slopes. Distinct zones also occur as altitude increases.
Some of the trees found here include paper
birch, alpine
fir, lodgepole
pine, black spruce,
white spruce,
trembling aspen,
balsam poplar,
water birch,
Alaska paper birch,
blue-green willow, bebb
willow, and net-veined willow. Other
plants include mountain aven, eriacaceous shrubs, sedge, cottongrass,
Labrador tea, fire snag, larkspur, forget-me-not, wooly lousewort, arnica,
hedysarum, white camas, purple mountain saxifrage, yellow mountain saxifrage,
alpine bearberry, arctic white heather, alpine bearberry and prickly
saxifrage.
Animals
As with the plants, the animal species to be found depend upon their
location in the ecozone. Alpine regions, lowland forests and wetlands
all have characteristic species.
Mammals
Large carnivores that are found here include black
bear, grizzly
bear, wolf
and lynx.
The large herbivores include Dall’s
sheep, caribou,
moose,
and mountain
goat. Small carnivores such as coyote,
red fox, least
weasel, mink,
wolverine,
muskrat,
and marten
can be found here, preying in part on arctic
ground squirrel, American
pika, hoary
marmot, beaver,
and brown lemming.
Birds
Some of the characteristic birds of prey are gyrfalcon,
golden eagle,
bald eagle,
osprey, northern
goshawk, boreal
owl, short-eared
owl, red-tailed
hawk, northern
harrier, American
kestrel, and merlin.
Shorebirds and seabirds that are found here include spotted
sandpiper, common
snipe, wandering
tattler, herring
gull, and mew gull.
The songbirds of the Taiga cordillera include common
redpoll, rusty
blackbird, gray-cheeked
thrush, tree swallow,
dark-eyed junco,
varied thrush,
raven, white-winged
crossbill, Lincoln’s
sparrow, Townsend’s
solitaire, water
pipit, violet-green
swallow, and gray
jay. Waterfowl such as Canada
geese, northern
pintail, mallard,
canvasback, and
arctic loon are
found here. Ruffed
grouse, spruce
grouse, northern
flicker, willow
ptarmigan, rock
ptarmigan, rock
ptarmigan, and white-tailed
ptarmigan are some of the birds of the forest.
Amphibians and Reptiles
The Taiga Cordillera is too far north for amphibians and reptiles.
Fish
Predators such as the northern pike feed on species including lake whitefish
and lake chub. Chinook salmon and chum salmon come in from the ocean
to spawn.
Mollucscs
Two of the mollusc species found in this ecozone are the muskeg
stagnicola and arctic-alpine
fingernail clam.
Humans
Only a few hundred people live here, and subsistence activities are
the norm. Otherwise, there is some tourism, but no major urban centres
or industries exist here.
 
|
|